Home | Surgical Weight Loss / Obesity Surgery | Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy | Laparoscopic Gastric Bypass | Laparoscopic Gastric Banding
LAPAROSCOPIC GASTRIC BYPASS
What is Laparoscopic Gastric Bypass?
Gastric bypass surgery makes the stomach smaller and allows food to bypass part of the small intestine. You will feel full more quickly than when your stomach was its original size. This reduces the amount of food intake and thus the total number of calories consumed. Bypassing part of the intestine also results in fewer calories being absorbed resulting in weight loss.
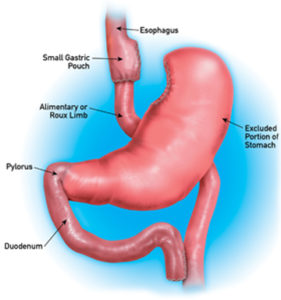
There are 2 types of Gastric Bypass
Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass
In a Roux-en-Y procedure, a small stomach pouch is created which reduces the amount of food you can eat. The smaller stomach is connected directly to the middle portion of the small intestine, bypassing the rest of the stomach and the upper portion of the small intestine.
Mini Gastric Bypass
The Mini Gastric Bypass procedure, is a modification of gastric bypass and has just one anaplasmosis ( Joint) and is, therefore, simpler to perform. The effects of both procedures on weight loss and other co-morbidities are nearly the same.
In our practice, we tend to reserve the Gastric Bypass for patients whose BMI is greater than 50 and associated with major co-morbidities especially Long-standing Type II Diabetes Mellitus.
Is Gastric Bypass for me?
You may be a candidate for Gastric Bypass if you have:
- BMI of > 40 kg/m2 with or without comorbidities or weight 42.5 kgs or more in excess of the normal
- BMI of 35-39.9 kg/m2 with one or more of the below co-morbidities
- BMI of 30-34.9 kg/m2 with at least two of the below co-morbidities
BMI Calculator
- The comorbidities may include:
- Life-threatening cardiopulmonary problems as coronary artery Disease (CAD), type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), obstructive sleep apnea, obesity hypoventilation syndrome, Pickwickian syndrome, non-alcoholic fatty acid disease or non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, hypertension, dyslipidemia, pseudotumor cerebrum, asthma, venous stasis disease, severe urinary incontinence, debilitating arthritis or obesity-related cardiomyopathy.
- Other obesity-induced physical problems that are interfering with lifestyle as musculoskeletal or neurologic or body size problems precluding or severely interfering with employment, family function and ambulation, and infertility in females.
- Made significant efforts at weight loss by participating in physician or professionally supervised weight loss programs and failed to achieve sustained weight loss.
Preparation prior to Gastric Bypass Surgery
- Set of Blood tests are required to evaluate Patient’s fitness for surgery
- An Ultrasound Scan of the abdomen is in order to evaluate size of Liver and presence of Gallstones
- A Gastroscopy may be required to evaluate presence of a Hiatal Hernia for patients getting Acid Reflux
- A 2-week Fat-free diet plan is advised to be followed strictly.
- Protein shakes 40grams and Multivitamins are advised to be taken 2 weeks prior to surgery to build up a reserve in anticipation of a relative lack of nutrition in the first two weeks after surgery when only liquids are allowed to be consumed.
How is Gastric Bypass performed?
The patient will be admitted to the hospital at least 3 hours prior to surgery time and is expected to stay Overnight.
The surgeon will make a series of small incisions in your upper abdomen, through which he will pass fine laparoscopic instruments and a camera. The expected length of surgery is around 2 hours.
Recovery and Discharge from the Hospital
When the patient is able to drink at least 2 litres of warm water in a day, Pain is under control and patients’ clinical condition is stable, It’s time to go home. You are encouraged to be mobile to accelerate recovery process and most patients are back to work 7 days after Laparoscopic Gastric Bypass.
Some patients may experience nausea or vomiting but medication is given to rectify this promptly. Some discomfort and limited mobility are also to be expected but prescribed medication is available to control this. You can be assured of immediate care and attention at all times.
When to call your Surgeon
- Persistent fever over 101F (39 C)
- Bleeding
- Increased abdominal swelling or pain
- Persistent nausea or vomiting
- Chills
- A persistent cough and shortness of breath
- Difficulty swallowing that does not go away within a few weeks
- Drainage from any incision
- Calf swelling or leg tenderness
Post-op dietary plan following Gastric Bypass
A well structured dietary guideline is designed to be strictly followed after the Surgery. Patient must stick to a liquid-based diet for 2 weeks after surgery. A soft diet follows for a further 2 weeks and about 4 to 5 weeks after the surgery, patient graduates to a 600 to 800 per day solid diet.
Home | Surgical Weight Loss / Obesity Surgery | Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy | Laparoscopic Gastric Bypass | Laparoscopic Gastric Banding
